ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
-
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by the progressive degeneration of neuronal populations and the simultaneous loss of memory and cognitive functions.
Neurite outgrowth in CORTICAL NEURONS
Progressive cell loss in neuronal populations is a pathological hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of new compounds which can mimic neurotrophin effects and have drug-like properties appears to be a promising strategy for the development of new therapeutics in neurodegenerative diseases. In addition to promoting neuronal survival, neurotrophins are also involved in neuronal differentiation and axonal outgrowth. The neurite outgrowth assay is used in neurobiology to study the neurotophic effect of a new compound.
-
Compound testing
Neuritogenesis is a critical aspect of neuronal maturation, health, plasticity and regeneration.
The measuring of neuritogenesis, including neurite outgrowth, is instrumental for the screening of the neuromodulatory, neuroprotective, neuroregenerative and neurotoxic effects of the compounds.
-
Endpoints
A fully automated analysis of neuritogenesis in 96 well plate of primary neuron cultures, which enables the quantification of :  the number of promoted neurite per neuron
the number of promoted neurite per neuron the total neurite length per neuron
the total neurite length per neuron the length of each major neurite of each neuron with or without its branches
the length of each major neurite of each neuron with or without its branches the number of branch points
the number of branch points
-
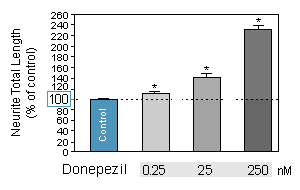
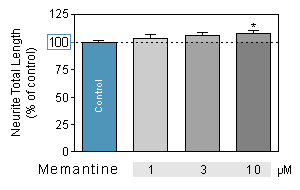
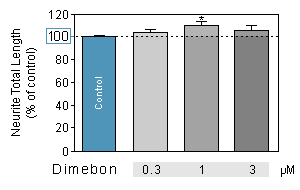
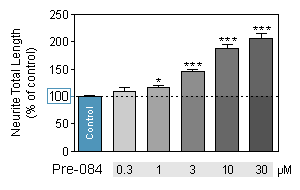
PROCOGNITIVE MODEL : quantification of the total length per neuron
-
Donepezil (Aricept®) is a centrally active small molecule used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and different cognitive disorders. -
Memantine is used for treating Alzheimer-type dementia. Memantine is an (NMDA)-receptor antagonist. Memantine works by blocking excess activity of glutamate. -
Dimebon inhibits brain cell death in animal models of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease. Multiple mechanisms of action: blocking the action of neurotoxic beta-amyloid proteins and inhibiting L-type calcium channels, modulating the action of AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors.
-
PRE-084 is a sigma receptor agonist, selective for the σ1 subtype. It has antidepressant actions in animal studies. PRE-084 increases the expression of GDNF. -
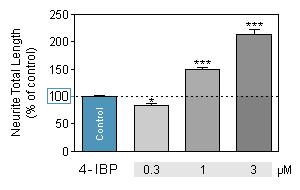
4-IBP is a σ1 Receptor Agonist. -
You could also be interested in
-
Neurite outgrowth
Neuritogenesis is a critical aspect of neuronal maturation, health, plasticity and regeneration.
-
Amyloid-β intoxication
The survival test exploits the natural tendency of cells to die in culture and is therefore used to assess the neuroprotective properties of your compounds.
Amyloid-β (in vivo)
Amyloid-β i.c.v injection induces learning deficits and a dysfunction of the cholinergic system.