Carrageenan mouse air pouch
-
-
Presentation
- Acute inflammation is a direct response of a tissue to injury. Inflammation is often characterized by symptoms such as redness, heat, swelling and/or pain.
The carrageenan mouse air pouch is an in vivo model that can be used to study acute and chronic inflammation. The inflammatory reaction is characterized by an infiltration of cells and an increase of pro-inflammatory mediators.
This model is extensively used to evaluate potential anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory drugs.
- Acute inflammation is a direct response of a tissue to injury. Inflammation is often characterized by symptoms such as redness, heat, swelling and/or pain.
-
Compound testing
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
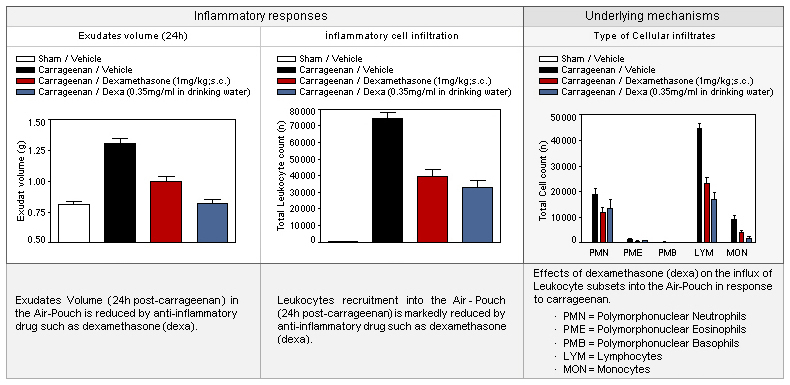
☐ Exudat volume
☐ Leukocyte count
☐ Cell count
-
Convenient in-vivo assay to simplify the screening of anti-inflammatory compounds
-
-
Highlights :
Shares similarities with the synovial cavity/fluid Provides insight to the underlying mechanism (type of Leukocytes involved) Short turn-around, high degree of reproducibility
You could also be interested in
-
MBP-induced EAE in the rat
EAE is a commonly used animal model which shares some degree of similarities with human multiple sclerosis.
RR-EAE in the rat
Relapsing/Remitting Multiple Sclerosis is the most frequent form of Multiple Sclerosis.
-
Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity in the rat
DTH is induced in female Lewis rats by subcutaneous injection of emulsion of ovalbumin / complete Freund's adjuvant.
Collagen-induced Arthritis in the rat
Collagen-induced arthritis is an experimental model sharing several clinical and pathological features with rheumatoid arthritis.
