ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
-
Contact dermatitis is an adverse cutaneous reaction resulting from direct contact with an irritant or allergic substance.
The skin’s reaction is an inflammation-driven process characterized by swollen itchy red rash or rough and dry skin.
OXAZOLONE model
Oxazolone is an allergic contact dermatitis inducer resulting in a type I cytokine response and has therefore been used as an animal model for identifying potential anti-inflammatory and immuno-modulating drugs.
-
Animal model of contact dermatitis
- NEUROFIT conducts screening and profiling of drug candidates in oxazolone-induced contact dermatitis.
Other animal models on inflammatory disorders are also available.
OXAZOLONE model - NEUROFIT conducts screening and profiling of drug candidates in oxazolone-induced contact dermatitis.
-
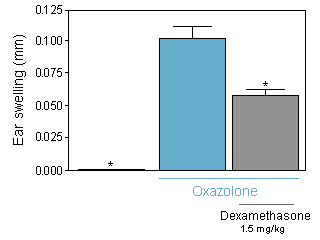
Dexamethasone
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat. Dexamethasone treatment signficantly reduced the reaction.
-
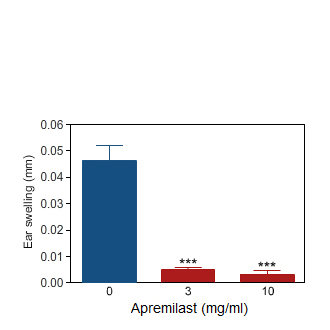
Apremilast
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar). Per os treatment with Apremilast markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
-
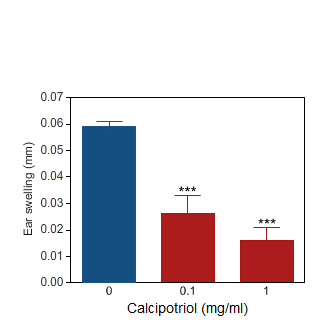
Calcipotriol
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar).Topical application of Calcipotriol markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
-
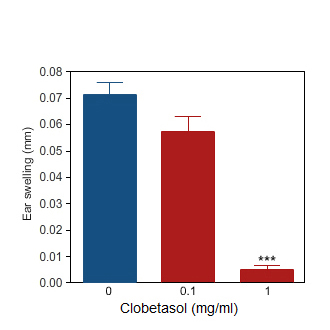
Clobetasol
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar).Topical application of Clobetasol markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
-
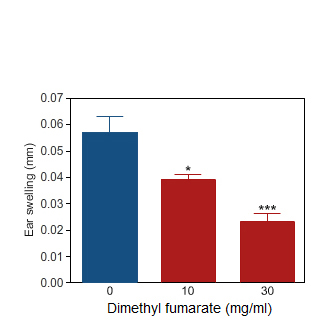
Dimethyl fumarate
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar). Per os treatment with Dimethyl fumarate markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
-
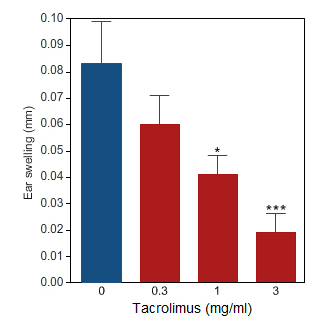
Tacrolimus
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar).Topical application of Tacrolimus markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
-
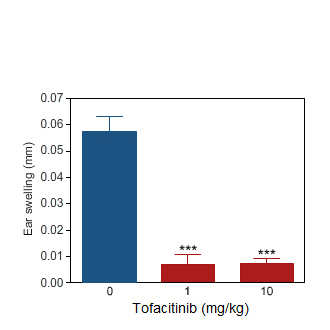
Tofacitinib
Ear swelling induced by oxazolone challenge in the rat (blue bar).Per os treatment with Tofacitinib markedly reduced the ear inflammation (red bars).
You could also be interested in
-
Ovalbumin model
The immune reaction is antigen specific and causes erythema, oedema and induration at the site of antigen.
-