PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHIES
-
Peripheral neuropathy is the result of damages of the peripheral nervous system. These troubles can be caused either by a trauma or diseases as for example diabetes.
NEUROFIT proposes animal and cellular models able to evaluate the neuroprotective activity of your coumpounds.
Sciatic Nerve Crush
Sciatic nerve crush is one of the most common models of peripheral nerve injury in rodents. Nerve damage results in rapid disruption of neuromuscular function which can be evidenced by electromyography measurement, gait analysis and histomorphometry of sciatic nerve fibers.
This model is used to assess the neuro-regenerative potential of test compounds (recovery of nerve function and axonal regeneration).
-
Compound testing
Neuro-regenerative drugs are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ g-ratio
☐ Axon size distribution profile in sural nerve
☐ Electromyography measurement : CMAP amplitude
☐ DWB : measure of imbalance weight distribution
-
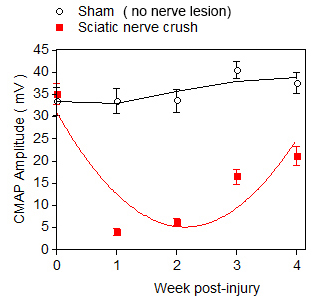
Electromyography measure
Time course of loss and recovery in Compound Muscle Action Potential (CMAP) following sciatic nerve crush.
-
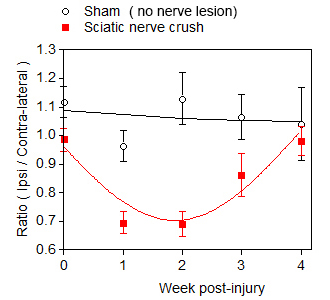
Gait analysis (weight bearing)
Nerve lesion-induced asymmetric weight bearing followed by progressive normalization of weight distribution.
-
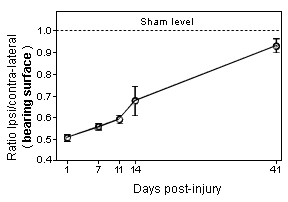
Graphs showing gait dysfunction as assessed by the measure of weight distribution on the four limbs of the mouse following sciatic nerve crush. Note that the dysfunction remains very pronounced 2 weeks after the nerve crush.
| |
-
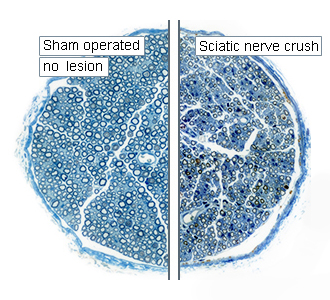
Comparative photomicrograph of tibial nerve sections showing the status of nerve fibers in Sham operated and sciatic nerve crush specimens at 4 weeks post-injury. -
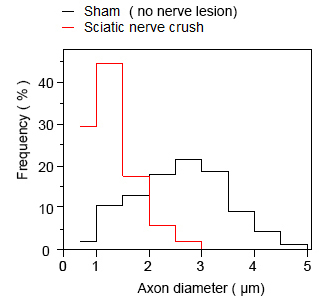
Nerve morphometry
(axon profile distribution)4 weeks after the lesion, axons with diameter ≥ 2.5 µm are not fully regenerated yet in lesioned nerve.
-
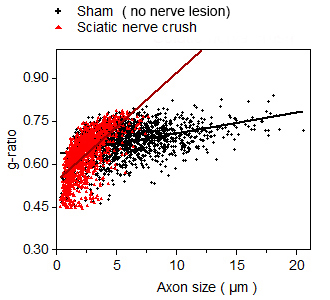
Nerve morphometry
(g-ratio: myelin thickness)4 weeks after the lesion, axons with diameter ≥ 2.5 µm in lesioned nerve show thinner myelin sheath* than those in sham nerve specimen.
(*, greater the g-ratio, thinner the myelin sheath thickness is)
-

Electrodiagnostic testing. -
-
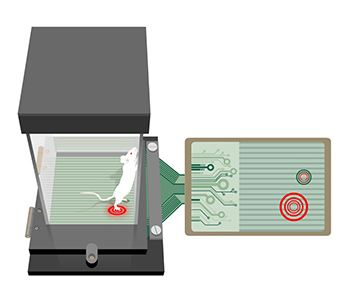
Schematic illustration of measure of imbalance weight distribution in freely moving animal.
-
-
You could also be interested in
-
Streptozotocin (STZ)
Diabetic neuropathy can be studied in rat following streptozotocin administration which induces a rapid and persistent hyperglycaemia.
-
IENF
The degeneration of intra-epidermal nerve fibers can be monitored and quantified in various animal models of peripheral neuropathy.

 VALIDATION DATA
VALIDATION DATA