Novel Object Recognition
-
-
Presentation
- The object recognition task in rodents is considered a test for evaluating working memory in rodents.
It is based on the spontaneous exploration of novel and familiar objects. Naive animals will spend more time exploring a novel object than a familiar one. When used in conjunction with pharmacological tools such as scopolamine that induces cognitive deficit (reduction in the recognition index), it becomes a useful model for screening compounds with memory enhancing properties.
- The object recognition task in rodents is considered a test for evaluating working memory in rodents.
-
Compound testing
Cognitive enhancers or disease modifiers are usually tested in this test but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints

Recognition index (time spent exploring the novel object)
-
-
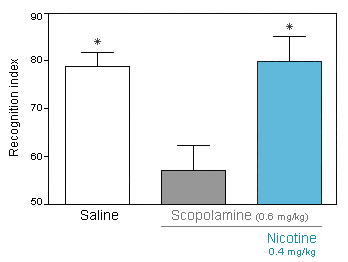
Reversal of Scopolamine-induced cognitive deficit in the novel object recognition assay by Nicotine. - Scopolamine and/or Nicotine are given at the beginning of the acquisition trial. Retention trial is performed 30 min after the acquisition trial.
Recognition index: proportion of time spent exploring the novel object.
- Scopolamine and/or Nicotine are given at the beginning of the acquisition trial. Retention trial is performed 30 min after the acquisition trial.
You could also be interested in
-
Passive avoidance
The Passive Avoidance is a fear-aggravated test used to assess short- or long-term memory.
T-Maze
The T-maze continuous alternation task is among the method implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice.
-
Amyloid β (cellular model)
Intoxication of neuronal cultures with Aβ.
Neurite outgrowth
Neurite outgrowth assay is used in neurobiology to study the neurotophic effect of a new compound.

 SCOPOLAMINE model
SCOPOLAMINE model