T-Maze Continuous Alternation Task (T-CAT) in mice
-
-
Presentation
- The T-maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) is one of the methods implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice. The procedure relies on the animal's natural behaviour to explore novelty and thus alternate between right and left arms.
When used in conjunction with pharmacological tools, the system allows us to evaluate the memory deficits (represented by a reduction in the number of alternations), thus providing with a useful model for screening compounds with cognitive enhancing properties.
- The T-maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) is one of the methods implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice. The procedure relies on the animal's natural behaviour to explore novelty and thus alternate between right and left arms.
-
Compound testing
Acute or subchronic treatment.
-
Endpoints

Percentage of alternation of mice in the T-maze.
-
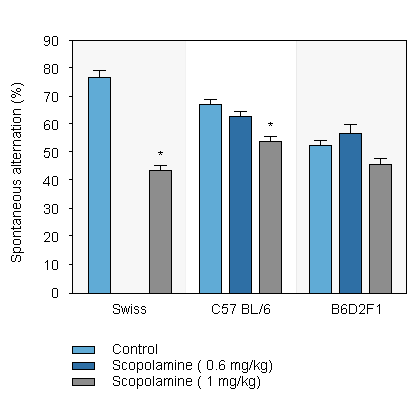
Deficits induced by scopolamine in 3 mouse strains as assayed in the T-maze -
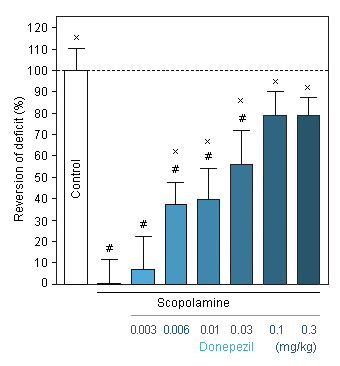
Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Donepezil (0.003 to 0.3 mg/kg) in Swiss mice in the T-maze.
-
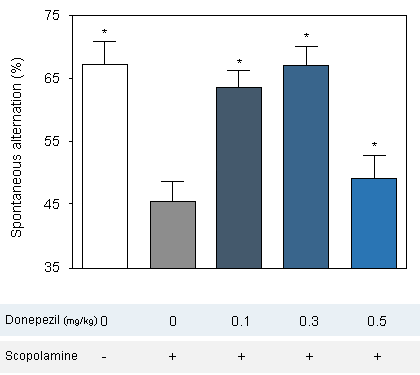
Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Donepezil (0.1 to 0.5 mg/kg) iin Swiss mice in the T-maze. -
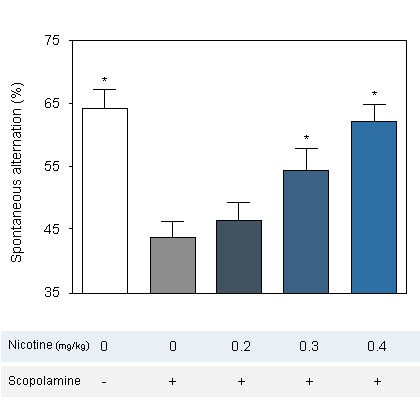
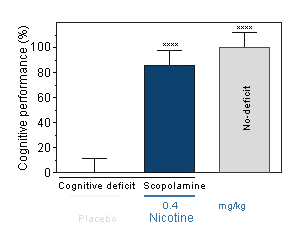
Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Nicotine in Swiss mice in the T-maze.
-
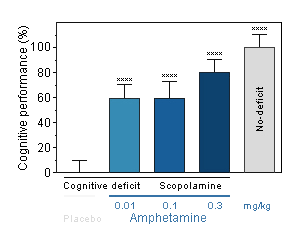
Amphetamine : Reversal effect of Amphetamine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
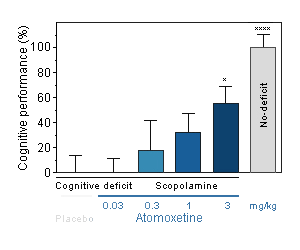
Atomoxetine : Reversal effect of Atomoxetine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
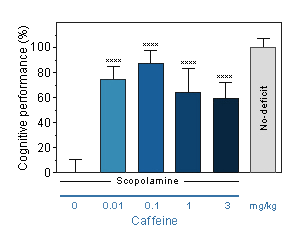
Caffeine : Reversal effect of Caffeine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
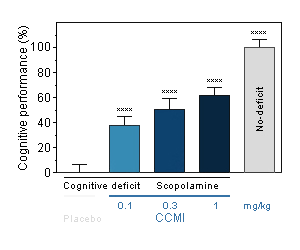
CCMI : Reversal effect of CCMI on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
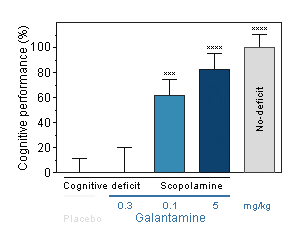
Galantamine : Reversal effect of Galantamine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
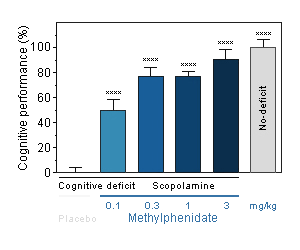
Methylphenidate : Reversal effect of Methylphenidate on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
Nicotine : Reversal effect of Nicotine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
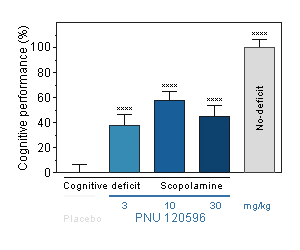
PNU120596 : Reversal effect of PNU120596 on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
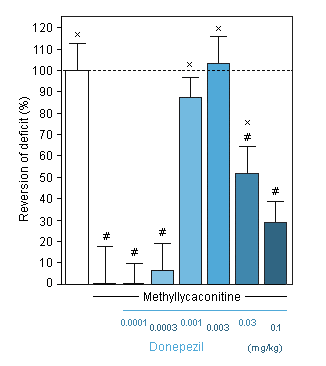
Donepezil : Reversion of Methyllycaconitine-induced cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse -
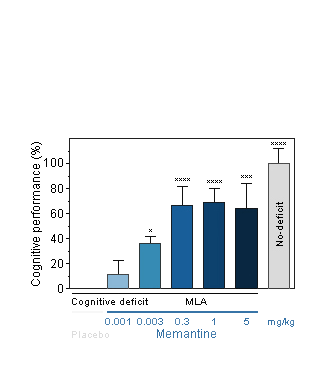
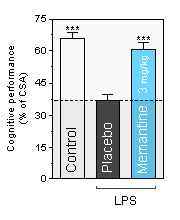
Memantine : Reversion of Methyllycaconitine-induced cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse
-
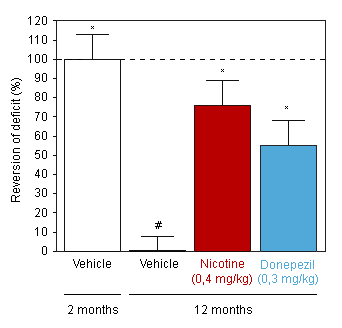
Nicotine - Donepezil : Reversion of Aging-related cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse
-
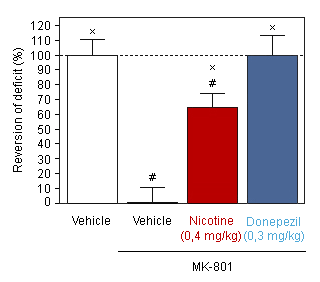
Nicotine - Donepezil : Reversion of MK-801-induced cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse
-
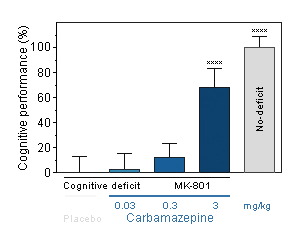
Carbamazepine : Reversal effect of Carbamazepine on cognitive deficit induced by MK-801 in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
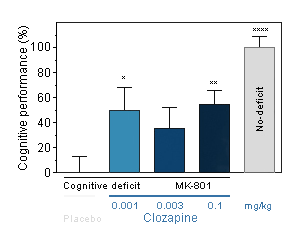
Clozapine : Reversal effect of Clozapine on cognitive deficit induced by MK-801 in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-Maze. -
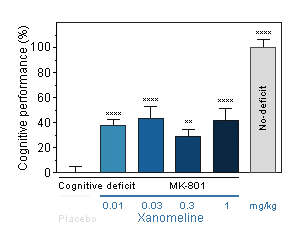
Xanomeline : Reversal effect of Xanomeline on cognitive deficit induced by MK-801 in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
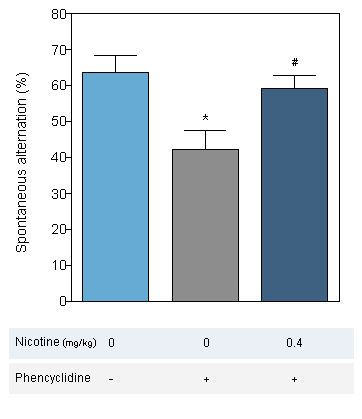
Nicotine : Reversion of Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse -
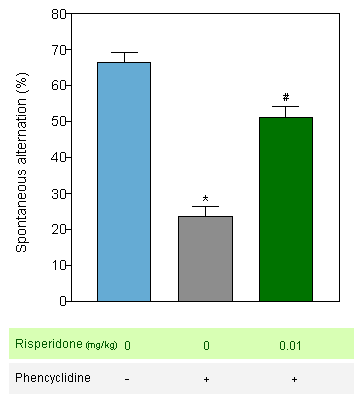
Risperidone : Reversion of Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficit in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse -
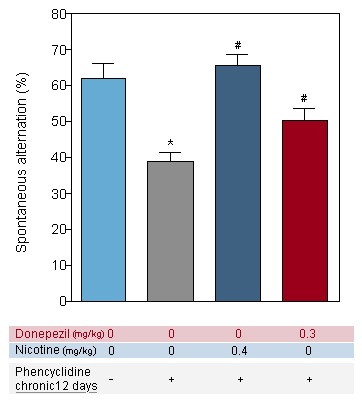
Nicotine and Donepezil : Reversion of Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficit (CHRONIC TREATMENT) in the T-Maze alternation task in the mouse
-
*** , statistically significant as compared to the Placebo condition
Memantine : Alzheimer's disease medication acting on the glutamatergic system by blocking NMDA receptors. -
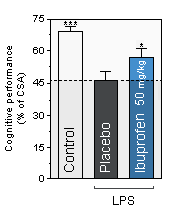
*, *** , statistically significant as compared to the Placebo condition
Ibuprofen : Anti-inflammatory drug. People treated with Ibuprofen for inflammatory conditions are reported to have lower rates of Alzheimer's disease. -
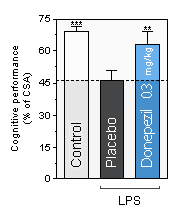
**, *** , statistically significant as compared to the Placebo condition
Donepezil : (Aricept) is a centrally active small molecule used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and different cognitive disorders.
You could also be interested in
-
Novel object recognition
The object recognition task in rodents is considered a test for evaluating working memory in rodents.
Passive avoidance
The Passive Avoidance is a fear-aggravated test used to assess short- or long-term memory.
-
Methyllycaconitine
MLA is an α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific antagonist with brain penetrance.
Age-associated cognitive deficit
Aged mice is the most representative of the human Alzheimer's disease.

 Scopolamine model
Scopolamine model