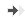brain inflammation-related cognitive deficit
Newsletter # 100

In vivo studies
■ Preclinical data from Neurofit indicated that 1 week treatment with cinnamaldehyde is sufficient to show therapeutic benefits in a mouse model of
-

*, p ≤ 0.05; ***, p ≤ 0.001 significantly different as compared to LPS / Placebo group (n = 10 mice per group). -
The Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge is used to model neuroinflammation associated withneurodegeneration such as inAlzheimer's disease 3 .
■ The graph shows that the LPS-challenge markedly impairs the cognitive function of mice as measured by reduced spontaneous alternations during the T-maze task (red vs white column). The decrease in the alternation reflects stereotypic and repetitive behavior, common cognitive symptoms indementia patients 4 . The treatment of LPS-challenged mice with Cinnamaldehyde (yellow columns) significantly increases the alternation level, thus thecognitive performance of mice.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS