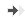Newsletter # 105

Animal models
-
Rapastinel modifies
CNS behavior
Left panel :
The graph shows the number of marbles buried by mice during a 20-minute-long session. 20 glass marbles (diameter: 1.5 cm) are spaced evenly along the walls of the homecage cage which contains about a 5 cm layer of fine sawdust bedding.
Placebo-treated mice bury about three-quarters of the marbles whereas those treated with anxiolytics or antidepressants bury significantly less. 120 minutes pre-treatment with Rapastinel induces a dose-dependent inhibition of marble burying behavior.
-
Right panel :
The graph shows the change in the spontaneous alternation of mice in the T-maze following treatment with different drugs. The spontaneous alternation paradigm represents a useful tool for cognitive evaluation (a higher rate of alternation reflects a better cognitive performance). Placebo-treated mice perform an alternation rate > 65% which is markedly reduced by treatment with NMDA antagonists such as Phencyclidine (also known under street names of peace pill, angel dust, crystal , etc...) and MK-801 (Dizocilpine). Rapastinel, with a proven CNS effect, does not significantly alter the spontaneous alternation performance of mice which suggests the absence of potential cognitive side effects.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS