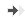Newsletter # 28

Animal models
-
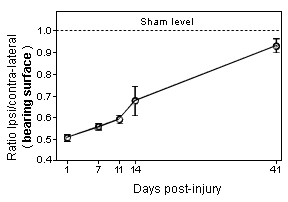
Graphs showing gait dysfunction as assessed by the measure of weight distribution on the four limbs of the mouse following sciatic nerve crush. Note that the dysfunction remains very pronounced 2 weeks after the nerve crush. -
-
 HISTOMORPHOMETRY data
HISTOMORPHOMETRY data
-
-
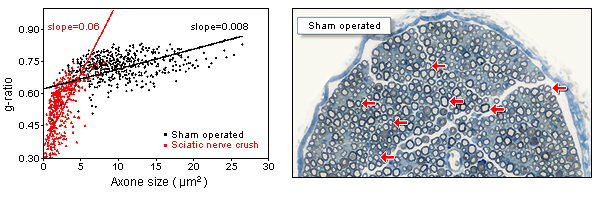
Comparative photomicrograph of sural nerve sections showing the difference in the status of nerve fibers of Sham operated and sciatic nerve crush specimens at 3 weeks post-injury.
-
Graph showing the disruption of g-ratio distribution profile in sural nerve following a sciatic nerve crush. In sham operated specimen, g-ratio (relative thickness of the myelin sheath) is relatively constant for axons of all size. Note the presence of large number of small and hypermyelinated axons following sciatic nerve crush (3 weeks post-injury).
-
-
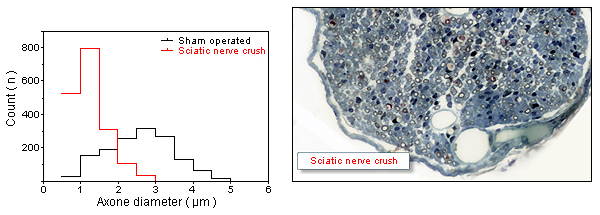
Note the marked absence of large caliber axons in the nerve crushed specimen.
-
Graph showing the disruption of axon size distribution profile in sural nerve following a sciatic nerve crush (3 weeks post-injury).
-
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY data
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY data
-
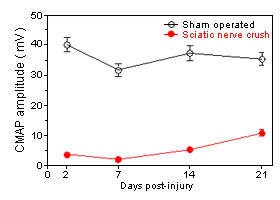
Note the presence of polyphasia and temporal dispersion in the CMAP at Day 14 post-injury. -
Time course of change in the amplitude of Compound Muscle Action Potential (CMAP) folowing Sciatic Nerve Crush. (3 weeks post-injury).
-
We look forward to hearing from you.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS