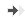Newsletter # 77

Catalepsy model
 In rodents, the neuroleptic drug haloperidol blocks the central dopamine transmission and induces catalepsy characterized by muscular rigidity and behavioral immobility (akinesia). The above similarities makes Haloperidol-induced catalepsy an useful test system for the screening of compounds that could alleviate the motor symptoms of PD. In rodents, the neuroleptic drug haloperidol blocks the central dopamine transmission and induces catalepsy characterized by muscular rigidity and behavioral immobility (akinesia). The above similarities makes Haloperidol-induced catalepsy an useful test system for the screening of compounds that could alleviate the motor symptoms of PD.
|
 The degree of inhibition/reversion of haloperidol–induced catalepsy can be used to measure the potential effect of your new drugs on akinesia symptoms of PD.
NEUROFIT has evaluated the effects of Levodopa (L-DOPA) and 8-(3-Chlorostyryl)caffeine (CSC) in this model. The degree of inhibition/reversion of haloperidol–induced catalepsy can be used to measure the potential effect of your new drugs on akinesia symptoms of PD.
NEUROFIT has evaluated the effects of Levodopa (L-DOPA) and 8-(3-Chlorostyryl)caffeine (CSC) in this model.
|
-
Time course of Haloperidol-induced catalepsy mice.
Treatment with CSC and L-DOPA markedly reduce haloperidol-induced catalepsy. -

-
Significant reduction of the catalepsy time at the plateau
is observed following the treatment of haloperidol-rats with CSC or L-DOPA during the stable phase (180-270min) can be observed. -

-
In addition to our Cellular models, consult also our Animal models in THERAPEUTIC AREA and TESTS sections at our website
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS