Newsletter # 09
Animal models
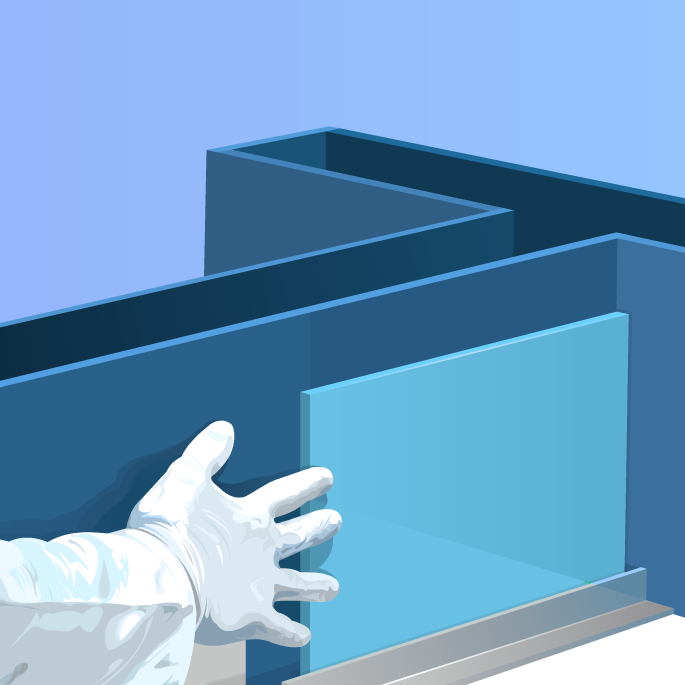
When used in conjunction with pharmacological tools such as scopolamine, the system allows to induce memory deficit (reduction in the number of alternation) useful as model for screening compounds with cognitive enhancing properties such as nicotine or donepezil.
-
Compound testing :Compound testing addresses the effect of acute treatment (typically 15-60 min before the implementation of the test) on the percentage of alternation of mice in the T-maze. Investigation of the effect of subchronic treatment is also possible.
-
Deficits induced by scopolamine in 3 mouse strains as assayed in the T-maze. -
We look forward to hearing from you.
-

Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Nicotine in Swiss mice. -
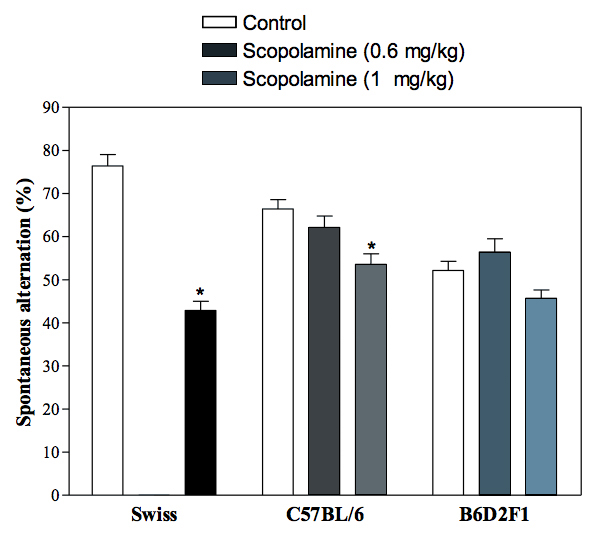
Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Donepezil in Swiss mice.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS