Newsletter # 10
Animal models
CIA has been used to study the pathogenesis of RA. This model is widely used to address questions of disease pathogenesis and to validate therapeutic targets. The chief pathological features of CIA include a proliferative synovitis with infiltration of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cells, pannus formation, cartilage degradation, erosion of bone, and fibrosis. As in RA, TNFalpha and interleukin IL-1beta are expressed in the arthritic joints, and blockade of these molecules results in a reduction of disease severity.
-
Compound testing :Arthritis is induced in female Lewis rats using Bovine type II collagen (CII) emulsified in complete Freund’s adjuvant. Each rat is given CII emulsion at day 0. Seven days later, a second injection was carried out (boost injection). Arthritis is monitored at day 7, 14, 17 and 21 post-immunization using the hind paws swelling as parameter. The size of the hind paw is reflected by water displacement (in g), which increases with swelling. Compound testing addresses the effect of treatment (typically starting on day 14) on the hind paws swelling.
-
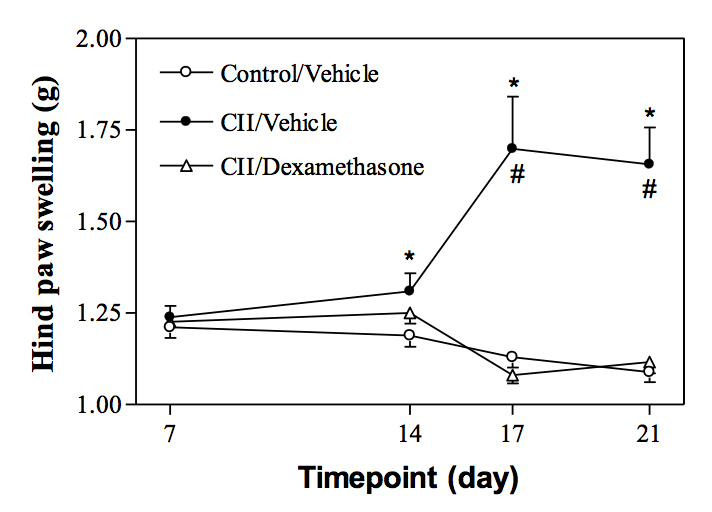
Collagen emulsion induced a significant hind paw swelling. Dexamethasone treatment (s.c., 1mg/kg, starting D14) is able to prevent this swelling. -
We look forward to hearing from you.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS