Newsletter # 13
Cellular models
-
In this assay, 9-day-old hippocampal neuron cultures are injured with the peptide β-amyloid 1-40 (Aβ 1-40). The neuroprotective effect of compounds is evaluated based on their ability to inhibit the damage to the neurons.
Neuronal survival is assessed by measuring MTT activity and /or neuronal death is assessed by measuring LDH activity in the media.
-
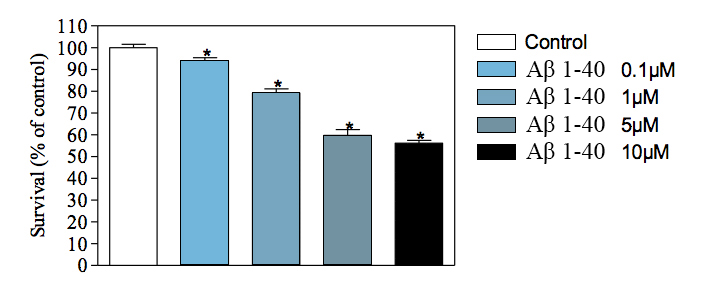
Reduced cell viability (MTT assay) in hippocampal neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of Aβ 1-40
* : significantly different as compared to control group -
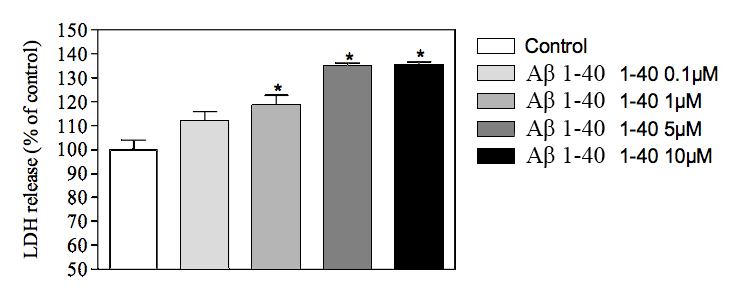
Increased cell death (LDH assay) in hippocampal neurons in response to increasing doses of Aβ 1-40
* : significantly different as compared to control group
-
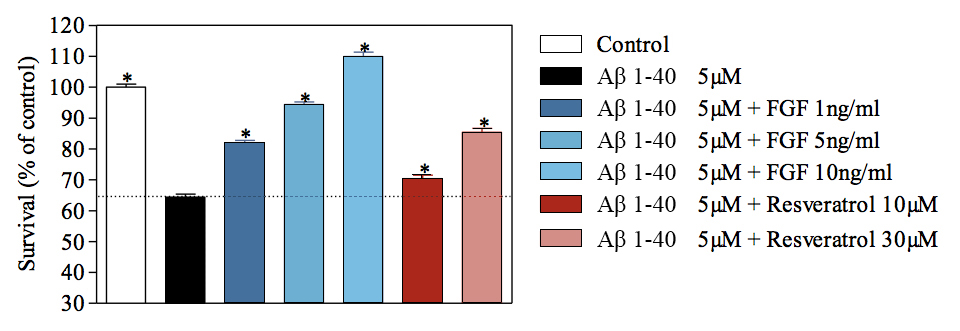
Prevention of Aβ 1-40 –induced neuronal injury by bFGF or by resveratrol as assessed by MTT assay in hippocampal cultures. bFGF (or reseveratrol) is added to culture media at the same time as Aβ 1-40 *: significantly different as compared to Aβ group -
We look forward to hearing from you.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS