Newsletter # 32
Animal models
Intra-cerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injections of fibrillated Amyloid-β (Aβ) in rats is associated with neuropathological features of AD. Faster and cost-effective than transgenic mice, this model is tailored to accelerate and aid drug discovery in the treatment of AD.
-
Effect of subchronic and single treatment with donepezil on the passive avoidance performance of i.c.v. Aβ-injected rats (2 weeks post-i.c.v. injection)
-
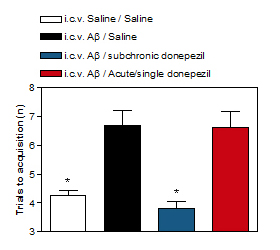
i.c.v. injection of Aβ impairs the acquisition of passive avoidance task.
Subchronic but not acute donepezil prevents this impairment. -
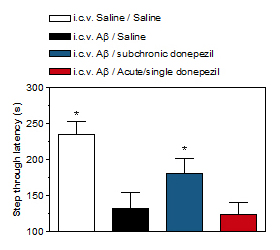
i.c.v. injection of Aβ disrupts the retention of passive avoidance.
Subchronic but not acute donepezil enhances the retention of passive avoidance in i.c.v. Aβ-injected rats.
-
We look forward to hearing from you.
Get in touch


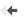 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS