AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also called Lou Gehrig’s disease or Charcot disease) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the gradual degeneration of motor neurons causing ascending paralysis and eventually leading to death.
SPINAL MOTOR NEURONS
Enhancing axonal growth is one of the strategies currently under investigation concerning ALS treatments and that’s why we propose our neurite outgrowth model on spinal motor neurons.
-
Compound testing
Neuroprotectant and compounds having a neurotrophic or neuroregenerative activity are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ Neuronal death
☐ Neuron survival
☐ Neurite length
-
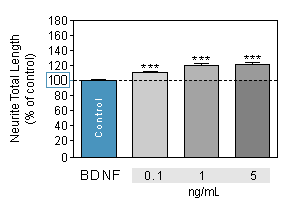
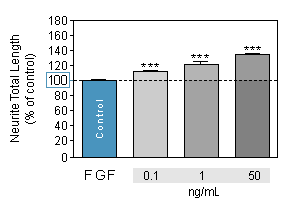
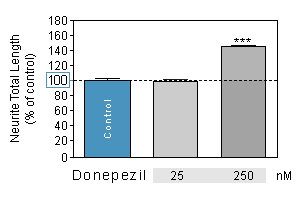
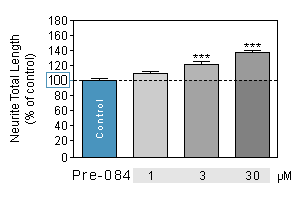
Effect of reference compounds on Neurite outgrowth in SPINAL NEURONS culture
-
BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors. BDNF acts on certain neurons of the CNS and the PNS, helping to support the survival of existing neurons, and encourage the growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses. -
FGFs are a family of growth factors involved in angiogenesis, embryonic development and various endocrine signaling pathways. -
Donepezil (Aricept®) is a centrally active small molecule used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and different cognitive disorders.
-
PRE-084 is a sigma receptor agonist, selective for the σ1 subtype. It has antidepressant actions in animal studies. PRE-084 increases the expression of GDNF.
-
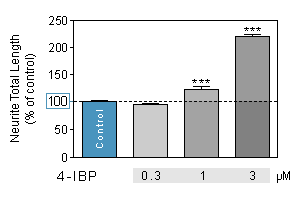
4-IBP is a σ1 Receptor Agonist.
You could also be interested in
-
Nerve-muscle coculture
The motor unit is an intricate pluricellular structure in which motor neurons and muscle fibers are dependant on each other.
Neurite outgrowth
Measure of neuritogenesis is instrumental for the screening of neuroprotective, neuroregenerative and neurotoxic effect of compounds.
-
Glutamate and NMDA
ALS model : a brief exposure to glutamate or NMDA causes neuronal death mainly by excessive stimulation of NMDA receptors.