PARKINSON'S DISEASE
-
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder featured by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.
The primary motor symptoms of patients with PD are muscular rigidity, akinesia-bradykinesia and resting tremor.
Haldol (catalepsy)
Catalepsy is a well-known symptom of Parkinson's disease. It is characterized by muscle rigidity and fixity of posture for a prolonged period of time (akinesia).
Haloperidol, a neuroleptic drug, induces catalepsy, and is thus used as a model for the screening of new compounds that could potentially reverse catalepsy and in that way improve certain symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
-
Compound testing
Anti-parkinsonian drugs are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ Haloperidol-induced catalepsy
☐ Akinesic symptoms of PD
-
The degree of inhibition / reversion of haloperidol-induced catalepsy is used to measure the potential effect of new drugs on akinesic symptoms of PD.
-
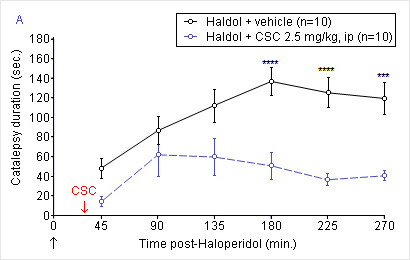
Graph A :
Time course of Haloperidol-induced catalepsy in the mouse.
Treatment with CSC markedly reduces haloperidol-induced catalepsy. -
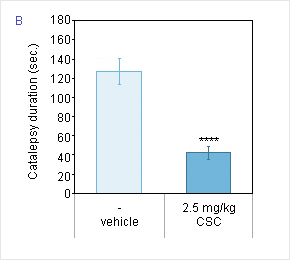
Graph B :
Reduction of haloperidol-induced catalepsy by CSC during the stable phase (180-270min).
You could also be interested in
-
6-OHDA (hemiparkinson)
6-hydroxydopamine is a neurotoxin widely used in lab animals to produce striatal dopamine depletion.
-
MPP+ and 6-OHDA (cellular model)
Ability of test compounds to inhibit MPP+ or 6-OHDA - induced cell damage in mesencephalic neuron cultures.
