ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
-
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. It is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by an extracellular accumulation of neurotoxic fibrillar amyloid beta peptide (Aβ). Compelling evidence indicates that the extracellular accumulation of Aβ is already present at the asymptomatic (preclinical) stage of AD. Thus, early intervention to prevent Aβ accumulation appears as an attractive strategy for AD treatment.
New functional assay for Amyloid lowering drugs
NEUROFIT has developed a functional neuronal assay that accumulates extracellular Aβ. The system is tailored to assess the efficiency of Aβ lowering drugs such as BACE inhibitors. In parallel, the assay also provides information about the potential safety or neurotoxicity of the tested drug.
-
Compound testing
Amyloid lowering drugs (e. g. BACE inhibitors) are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ Production of Aβ 1-42
☐ Survival of hippocampal neurons
-
BACE inhibitor screening assay
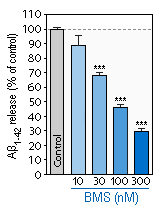
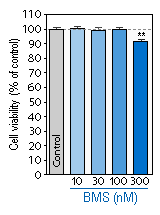
- The example below illustrates the inhibition of Aβ production by BMS-299897 (γ-secretase inhibitor) in cultures of hippocampal neurons (Left Panel). The Right panel indicates that BMS-299897 becomes neurotoxic at concentration ≥ 300 nM.
☐ BMS-299897
-
*** statistically significant as compared to the Control.
Inhibition of production of Aβ1-42 by BMS-299897 in cultures of hippocampal neurons. -
** statistically significant as compared to the Control.
Effect of BMS-299897 on the survival of hippocampal neurons in cultures.
You could also be interested in
-
Viability and survival test
This test exploits the natural tendency of cells to die in culture and is used to assess the neuroprotective properties of compounds.
T-Maze
The T-Maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) is among the method implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice.
Brain inflammation
Astrocytes and microglia are key players in neuroinflammation since they release wide variety of proinflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide, cytokines and chemokines.
-
Amyloid β (animal model)
Amyloid-β i.c.v injection induces learning deficits and a dysfunction of the cholinergic system.
Aged mice
This model is probably the most representative of the human Alzheimer's disease.
LPS induced inflammation
Translational in vivo model of inflammation-induced cognitive deficit.