Viability and survival test
-
-
Presentation
- The survival test exploits the natural tendency of cells to die in culture and is therefore used to assess the neuroprotective properties of your compounds. This test can be combined with various cell types depending on the pathology you target to assess the neuroprotective effect of your compounds.
-
Compound testing
Neuroprotective compounds are usually evaluated in this test but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints

Neuronal death assessed by LDH activity 
Neuronal survival measured by MTT activity
-
Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. It is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by an extracellular accumulation of neurotoxic fibrillar amyloid beta peptide (Aβ). Intoxication of neuronal cultures with Aβ has been widely used to understand some of the mechanisms of cell death in AD and thus represents an instrumental in-vitro system to evaluate the efficiency of neuroprotective drug candidates.
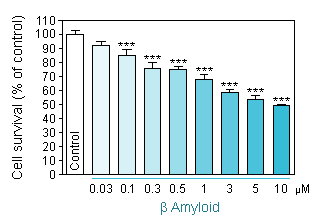
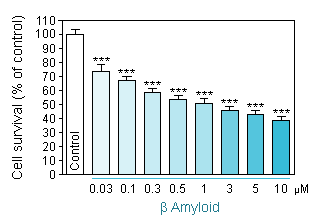
Dose response toxicity of Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42 on primary cultures of hippocampal neurons.

Aβ 1-40 intoxication using two different neuronal density per well. -
Reduced cell viability (MTT assay) in hippocampal neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of Aβ 1-40 at a cellular density of 35 000 neurons per well. -
Reduced cell viability (MTT assay) in hippocampal neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of Aβ 1-40 at a cellular density of 10 000 neurons per well.
-

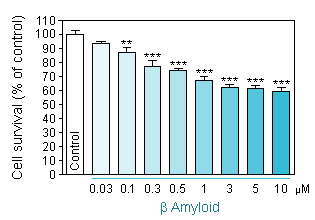
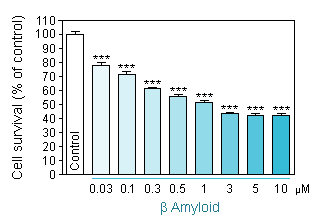
Aβ 1-42 intoxication using two different neuronal density per well -
Reduced cell viability (MTT assay) in hippocampal neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of Aβ 1-42 at a cellular density of 35 000 neurons per well. -
Reduced cell viability (MTT assay) in hippocampal neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of Aβ 1-42 at a cellular density of 10 000 neurons per well.
Neuroprotective effect of reference compound
-
against damage induced by Aβ 1-40 or Aβ 1-42 on primary culture of hippocampal neurons

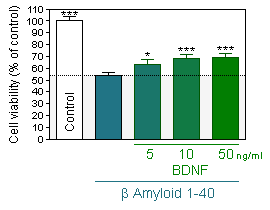
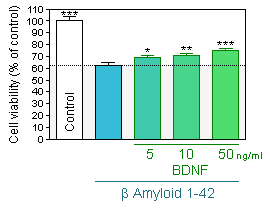
BDNF protection
-
Prevention of Aβ 1-40-induced neuronal injury by pretreatment with BDNF as assessed by MTT assay in hippocampal neuron cultures -
Prevention of Aβ 1-42-induced neuronal injury by pretreatment with BDNF as assessed by MTT assay in hippocampal neuron cultures
-

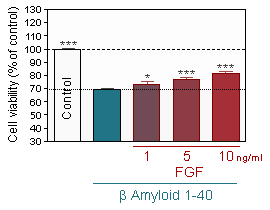
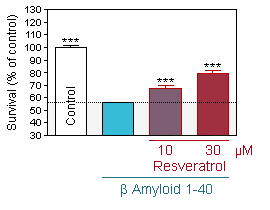
bFGF and Resveratrol protection
-
Prevention of Aβ 1-40-induced neuronal injury by pretreatment with b FGF as assessed by MTT assay in hippocampal neuron cultures -
Prevention of Aβ 1-40-induced neuronal injury by pretreatment with Resveratrol as assessed by MTT assay in hippocampal neuron cultures
References :
-
Resende R, Pereira C, Agostinho P, Vieira AP, Malva JO, Oliveira CR.
Susceptibility of hippocampal neurons to Abeta peptide toxicity is associated with perturbation of Ca2+ homeostasis.
Brain Res. 2007 Apr 27;1143:11-21. Epub 2007 Jan 27.Hirai K, Hayako H, Kato K, Miyamoto M.
Idebenone protects hippocampal neurons against amyloid beta-peptide-induced neurotoxicity in rat primary cultures.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;358(5):582-5.Jarvis K, Assis-Nascimento P, Mudd LM, Montague JR.
Beta-amyloid toxicity and reversal in embryonic rat septal neurons.
Neurosci Lett. 2007 Aug 23;423(3):184-8. Epub 2007 Aug 9.Han YS, Zheng WH, Bastianetto S, Chabot JG, Quirion R.
Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons: involvement of protein kinase C.
Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Mar;141(6):997-1005.
Glutamate excitotoxicity is involved in various neurodegenerative diseases such as spinal cord injury, stroke, traumatic brain injury, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease and also Huntington's disease.
In vitro, a brief exposure to glutamate causes neuronal death mainly by excessive stimulation of NMDA receptors.
-
13-day-old cortical neuron cultures are injured by an acute intoxication with glutamate.
The neuroprotective effect of compounds is evaluated based on their ability to inhibit on this damage. In the pre-treatment protocol, test compound is added 24h before intoxication and in the post-treatment one, test compound is added immediately after intoxication. Neuronal death is assessed by measuring LDH activity in the media at 24h after glutamate exposure.
-
12-day-old cortical neuron cultures are injured by an acute intoxication with NMDA. The neuroprotective effect of compounds is evaluated based on their ability to inhibit on this damage. In the pre-treatment protocol, test compound is added 24h before intoxication and in the post-treatment one, test compound is added immediately after intoxication. Neuronal death is assessed by measuring LDH activity in the media at 48h after NMDA exposure.
-
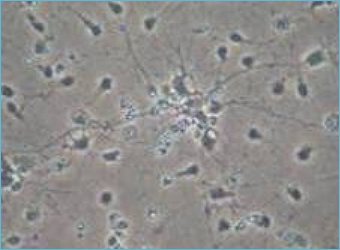
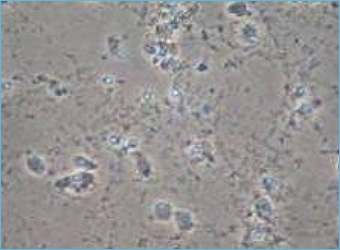
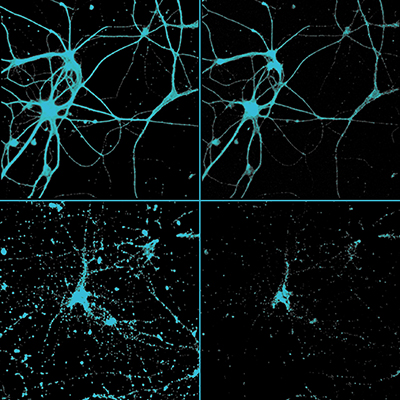
13-day old culture of cortical neuron on control condition. -
13-day old culture of cortical neuron injured by glutamate (10min, 75µM).
-

GLUTAMATE: 35,000 neurons per well
-
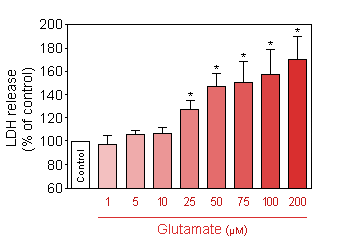
Release of LDH (CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay, Promega) in response to increasing doses of acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron. -
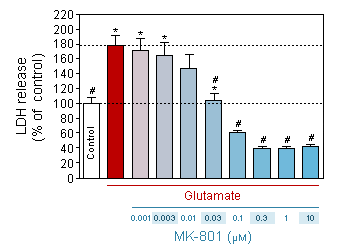
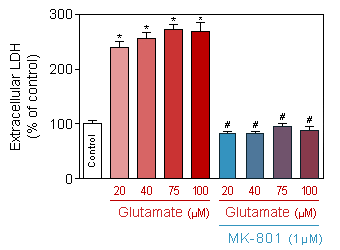
Effect of MK-801 on neuronal death induced by glutamate (75 µM, 10 min).
* p<0.05 compare the control group;
# p<0.05 compare the intoxicated group -
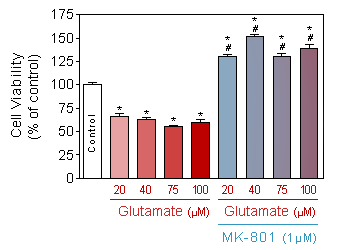
Evaluation of neuronal viability (Quantification of the presence of ATP by CellTiter Glo, Promega) in response to increasing doses of acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of 1µM of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the control group;
# p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
-
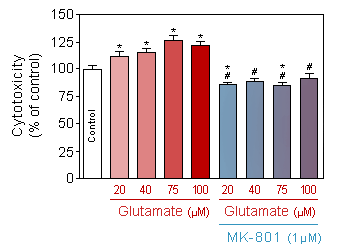
Evaluation of neuronal toxicity (quantification of binding of cell impermeant cyanine dye to dsDNA by CellTox Green, Promega) in response to increasing doses of acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of 1µM of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the control group;
# p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
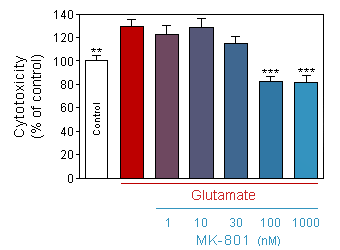
Evaluation of neuronal toxicity (quantification of binding of cell impermeant cyanine dye to dsDNA by CellTox Green, Promega) in response to acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
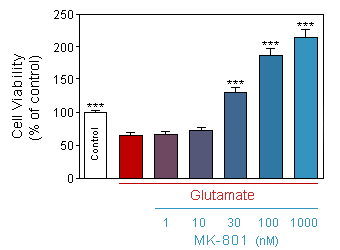
Evaluation of neuronal viability (Quantification of the presence of ATP by CellTiter Glo, Promega) in response to acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
-

GLUTAMATE: 10,000 neurons per well
-
Release of LDH (CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay, Promega) in response to increasing doses of acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of 1µM of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the control group;
# p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
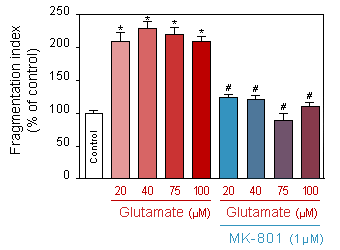
Effect of increased doses of acute (10min) glutamate on neurite network of 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of 1µM of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the control group;
# p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
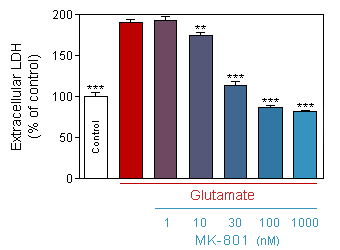
Release of LDH (CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay, Promega) in response to acute (10 min) glutamate intoxication on 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
-
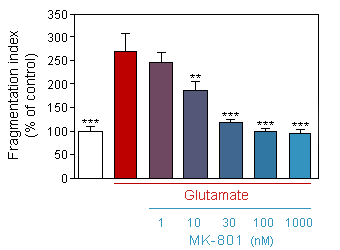
Effect of acute (10min) glutamate on neurite network of 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
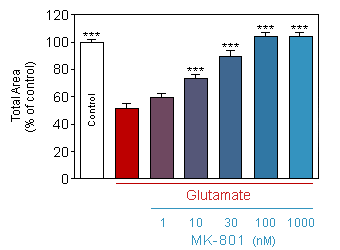
Effect of acute (10min) glutamate on total area of neurite network of 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
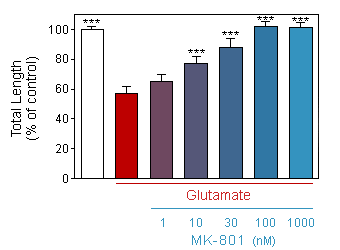
Effect of acute (10min) glutamate on total length of neurite of 13-day old culture of cortical neuron, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
 |
-
-
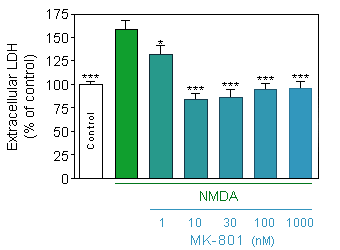
Release of LDH (CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay, Promega) in response to acute (75µM, 10 min) NMDA intoxication on 12-day old culture of cortical neuron at density of 10000 cells/well, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
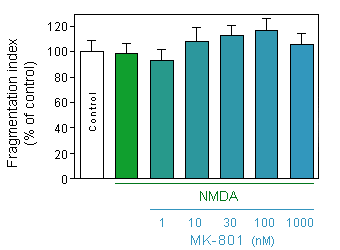
Evaluation of neuronal toxicity (quantification of binding of cell impermeant cyanine dye to dsDNA by CellTox Green, Promega) in response to acute (75µM, 10 min) NMDA intoxication on 12-day old culture of cortical neuron at density of 35000 cells/well, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
-
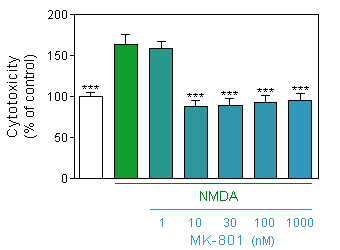
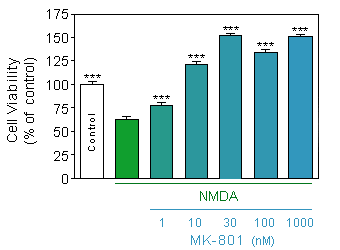
Evaluation of neuronal viability (Quantification of the presence of ATP by CellTiter Glo, Promega) in response to acute (75µM, 10 min) NMDA intoxication on 12-day old culture of cortical neuron at density of 35000 cells/well, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group -
Effect of acute (75µM, 10min) NMDA on neurite network of 12-day old culture of cortical neuron at density of 10000 cells/well, in presence or absence of increasing doses of MK-801.
* p<0.05 compare the corresponding glutamate group
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder with motor symptoms caused by the loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the striatum.
Compound testing addresses the ability of test compounds to inhibit MPP+ or 6-OHDA - induced cell damage in mesencephalic neuron cultures as assessed by immunostainting of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons.
-
Dose response toxicity of MPP+ and 6-OHDA on primary cultures of mesencephalic neurons
-
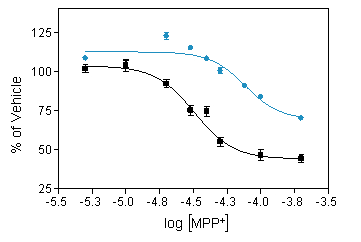
Reduced number of TH positive neurons ( ■ ) and cell viability (MTT assay,● ) in mesencephalic neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of MPP+. -
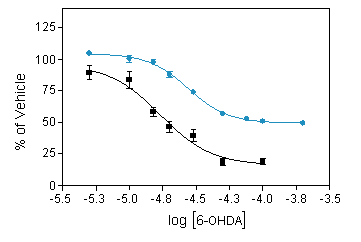
Reduced number of TH positive neurons ( ■ ) and cell viability (MTT assay,● ) in mesencephalic neuron culture in response to increasing concentration of 6-OHDA.
-

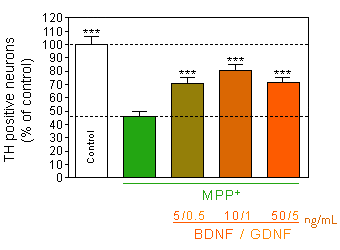
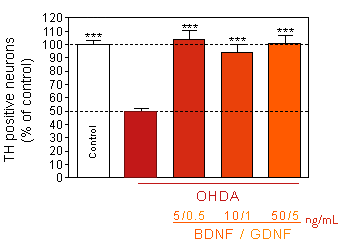
BDNF-GDNF : stimulation of neurotrophin pathways
-
Prevention of MPP+ -induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with mixture of BDNF-GDNF. -
Prevention of 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with mixture of BDNF-GDNF.
-

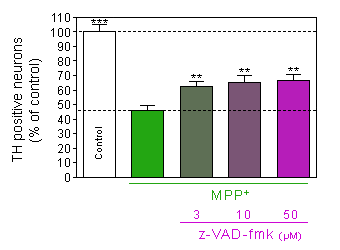
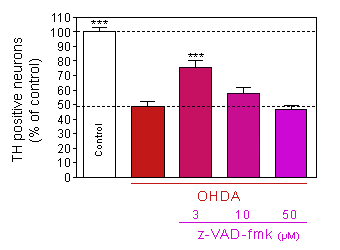
z-VAD-fmk : inhibition of caspase pathway
-
Prevention of MPP+ -induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with z-VAD-fmk, a caspase inhibitor. -
Prevention of 6-OHDA–induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with z-VAD-fmk, a caspase inhibitor.
-

N-acetyl-cystein : inhibition of oxidative stress
-
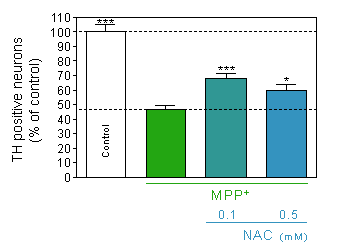
Prevention of MPP+ -induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetyl-cystein. -
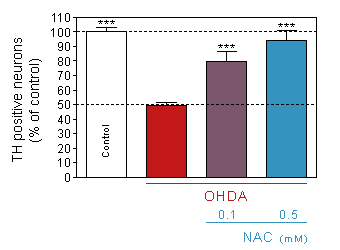
Prevention of 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neurons death
by pretreatment with the antioxidant N-acetyl-cystein.
You could also be interested in
-
Brain inflammation
Neuroinflammation is a critical process in different neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, MS ...
Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder.
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Neurodegenerative disease characterized by the gradual degeneration of motor neurons causing ascending paralysis and leading to death.
Parkinson’s disease
Neurodegenerative disorder featured by the loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra.

 β-AMYLOID-INDUCED NEUROTOXICITY in rat hippocampal neurons
β-AMYLOID-INDUCED NEUROTOXICITY in rat hippocampal neurons