Newsletter # 119

In vivo studies
Cobenfy, a groundbreaking pharmacological combination of Xanomeline and Trospium, represents the first FDA-approved drug targeting schizophrenia with a non-dopaminergic blocking mechanism. This innovative treatment addresses both the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, offering a new therapeutic avenue for a condition with limited effective options.
Cognitive impairment is a hallmark of schizophrenia and serves as a critical predictor of prognosis and long-term outcomes. Despite its central role in the disease, there are currently no approved pharmacological treatments specifically targeting cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
Cognitive impairment is a hallmark of schizophrenia and serves as a critical predictor of prognosis and long-term outcomes. Despite its central role in the disease, there are currently no approved pharmacological treatments specifically targeting cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
Emerging preclinical data from Neurofit demonstrate that Cobenfy significantly improves cognitive performance in a dose-dependent manner in a well-established mouse model of schizophrenia. These promising results suggest that Cobenfy has the potential to uniquely modulate cognitive dysfunction, a major unmet need in the treatment of schizophrenia.
This preliminary finding paves the way for the development of therapies that can improve cognitive outcomes for patients with schizophrenia, potentially revolutionizing the standard of care for this complex and debilitating disorder.
This preliminary finding paves the way for the development of therapies that can improve cognitive outcomes for patients with schizophrenia, potentially revolutionizing the standard of care for this complex and debilitating disorder.
-
 *, **and *** respectively indicate p ≤ 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001, as compared to red column.
*, **and *** respectively indicate p ≤ 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001, as compared to red column.
[10 mg/kg xanomeline + 4 mg/kg Trospium] is the estimated mouse equivalent dose, derived using body surface area scaling for a single Cobenfy (50 mg/20 mg) capsule taken by a 60 kg man.
-
Improvement of MK-801-induced cognitive deficit by Cobenfy
The graphs depict mice's cognitive performance through spontaneous alternation in the T-maze — a widely employed test for assessing a rodents' cognitive behavior in a single session. Higher spontaneous alternation rates correlate with greater cognitive performance. A significant reduction below the chance level (50%) signals repetitive insistence (stereotypy) on the same T-maze arm visit, indicating a cognitive deficit, which is a core symptom seen in conditions like dementia or schizophrenia.
MK-801 acts as an NMDA receptor antagonist, inducing symptoms akin to schizophrenia and cognitive impairment. Evidenced by reduced spontaneous alternations in mice (white vs black column), indicative of stereotypy, MK-801 leads to cognitive deficits.
Cobenfy administration demonstrates a dose-dependent improvement in spontaneous alternation performance in PCP-treated mice, enhancing cognitive ability (Red vs blue-green columns).

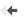 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS