Newsletter # 55

Animal drug screening model
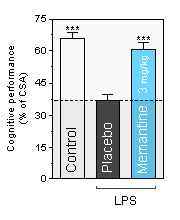
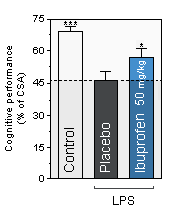
NEUROFIT offers a translational in vivo model of inflammation-induced cognitive deficit. Inflammation is produced in mice by single administration of a non-septic dose of LPS. The model has proved to be useful in demonstrating the clinical effect of drugs or compounds of different mechanisms.
-
Cognitive performance is assessed as the level of spontaneous and continuous alternation in the T-maze.
A lower alternation score represents lower cognitive performance.
CSA : Continuous and Spontaneous Alternation. -
*** , statistically significant as compared to the Placebo condition
Memantine : Alzheimer's disease medication acting on the glutamatergic system by blocking NMDA receptors. -
-
*, *** , statistically significant as compared to the Placebo condition
Ibuprofen : Anti-inflammatory drug. People treated with Ibuprofen for inflammatory conditions are reported to have lower rates of Alzheimer's disease.
Get in touch


 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS
 Memantine
Memantine